Prism adaptation treatment improves rehabilitation outcomes in people with spatial neglect
Funding: Kessler Foundation, Wallerstein Foundation for Geriatric Improvement
Performing daily sessions of prism adaptation therapy during rehabilitation results in higher functional and cognitive independence scores for stroke survivors
East Hanover, NJ. May 25, 2021. A team of experts in post-stroke neurorehabilitation confirmed that including prism adaptation treatment in standard of care for patients with post-stroke spatial neglect improved functional and cognitive outcomes according to the Functional Independence Measure®. The article, “Prism Adaptation Treatment Improves Inpatient Rehabilitation Outcome in Individuals with Spatial Neglect: A Retrospective Matched Control Study” (doi: 10.1016/j.arrct.2021.100130.
was published in Archives of Rehabilitation Research and Clinical Translation on May 19, 2021.
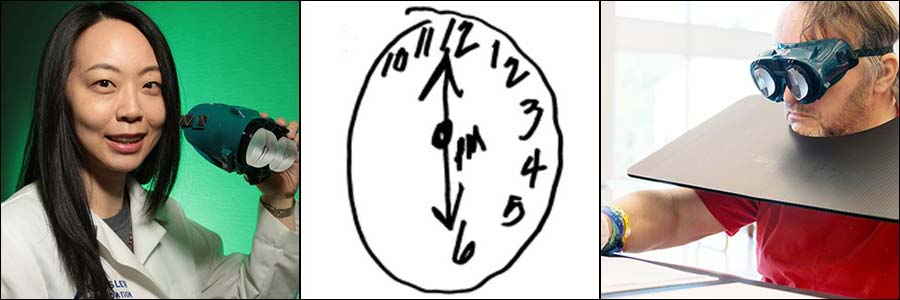
From left - Dr. Chen holding a pair of prism goggles used in prism adaptation treatment.
Center - A clock face drawn by a person with left-sided spatial neglect following right brain stroke.
Right - A research participant wearing prism goggles performs a task during prism adaptation treatment.
The authors are Peii Chen, PhD , and Emma Kaplan, BS , of Kessler Foundation’s Center for Stroke Rehabilitation Research; Nicole Diaz-Segarra, MD, of Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation; Kimberly Hreha, EdD, OTR/L, of the University of Texas Medical Branch; and A.M. Barrett, MD, of the Atlanta VA Health Care System. Dr. Chen also has an academic appointment at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School and Dr. Barrett has an academic appointment at Emory University School of Medicine.
Recent research by Dr. Chen’s group shows that after a stroke, approximately 30 percent of people experience spatial neglect, a neurological disorder that disrupts a person’s 'internal GPS', causing them to have difficulties in navigating their environment. Spatial neglect can also affect people with other types of brain injuries. Symptoms include poor balance and navigation as well as impediments in reading and memory. In addition, spatial neglect slows rehabilitation progress and functional recovery, and increases the risk for injury.
Prism adaptation treatment is a very promising therapy for spatial neglect, with some studies indicating that its beneficial effects may last years. During prism adaptation, people wear goggles equipped with optical prisms that shift their motor movements toward the neglected side. Through a ten-session program, individuals regain some ability to function in the neglected space.
In this video, Dr. Chen demonstrates prism adaptation treatment and how it works.
However, prism adaptation treatment has only been tested as an auxiliary therapy, with little data available regarding its effectiveness when integrated into the standard of care for people with spatial neglect.
In this study, researchers analyzed data from patients with spatial neglect at 14 rehabilitation hospitals where Kessler Foundation Prism Adaptation Treatment (KF-PAT®) was implemented in occupational therapy. They compared the outcomes of patients who received 8 to 12 daily sessions of prism adaptation treatment to patients who were untreated. The primary outcome measurable was the Functional Independence Measure (FIM®) and the secondary measurable was discharge destination.
“Our results clearly demonstrated that prism adaptation treatment enhances rehabilitation outcome,” said Dr. Chen, senior research scientist at Kessler Foundation. “The treated group showed reliably higher scores than the untreated group in total functional independence and cognitive functional independence.” She adds, “This is extremely encouraging evidence that integrating prism adaptation into standard of care for people with spatial neglect is beneficial.”
Study results did not show a significant effect in the rate of return-home after discharge, and the authors note that more research on prism adaptation treatment in this population is needed to further clarify how to optimize its effectiveness.A research participant wearing prism goggles performs a task during prism adaptation treatment
Learn more about tools for assessing and treating spatial neglect at Kessler Foundation Learning Center (https: www.kflearn.org) and https://kesslerfoundation.org/research/stroke/rehabilitation/spatial-neglect
Relevant articles:
Esposito, E., Shekhtman, G., & Chen, P. (2020). Prevalence of spatial neglect post stroke: A systematic review. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. doi:10.1016/j.rehab.2020.10.010
Funding sources: Kessler Foundation and Wallerstein Foundation for Geriatric Improvement.
About Kessler Foundation: Kessler Foundation, a major nonprofit organization in the field of disability, is a global leader in rehabilitation research that seeks to improve cognition, mobility, and long-term outcomes, including employment, for people with neurological disabilities caused by diseases and injuries of the brain and spinal cord. Kessler Foundation leads the nation in funding innovative programs that expand opportunities for employment for people with disabilities.